The importance of pollination in your vegetable garden: how to attract pollinators for beginners

The Importance of Pollination in Your Vegetable Garden
Pollination plays a crucial role in the flourishing of your vegetable garden. Without it, a wide array of plants may fail to produce the fruits and vegetables that are essential to our diets. For instance, vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers depend heavily on pollination to set fruit. When we talk about pollination, we’re talking about a fascinating interaction between plants and various creatures, primarily insects, that can dramatically affect your garden’s productivity.
Why is Pollination Important?
Understanding the significance of pollination can enhance your gardening efforts and ultimately lead to a bountiful harvest. Here are some critical reasons why pollination is vital:
- Increases Crop Yields: Many of our beloved vegetables, including squash and eggplant, need pollinators to ensure effective fruit development. Pollinators like bees transfer pollen from one flower to another, initiating the fertilization process that leads to fruit production.
- Enhances Biodiversity: A diverse garden not only yields a greater variety of vegetables but also attracts an array of pollinators. From honeybees to butterflies, a thriving garden teems with life, enriching the local ecosystem and making it more resilient to pests and diseases.
- Improves Plant Health: Healthy pollination leads to stronger plants. For example, a well-pollinated pumpkin may produce larger fruits, as opposed to those with insufficient pollination that tend to be small and misshapen.
For novice gardeners, attracting pollinators might seem challenging, but you can create an inviting habitat by implementing a few straightforward strategies. Here are some effective methods:
- Native Plants: Incorporating native plants into your garden is a natural way to attract local pollinators. Plants such as coneflowers and black-eyed Susans not only thrive in your local climate but also serve as reliable food sources for bees and butterflies.
- Flowering Plants: Choose a diverse selection of flowering plants to ensure there are blooms available throughout the growing season. Flowers like calendula, zinnias, and sunflowers can provide nectar and pollen for pollinators during critical times.
- Water Sources: Adding small water features, like birdbaths or shallow trays filled with pebbles and water, can be a refreshing oasis for thirsty pollinators. Even a simple dish of water can attract beneficial insects, particularly in hot months.
By diving into these strategies, you can not only elevate your gardening experience but also enhance the well-being of your local environment. Each small change contributes to a larger effort in supporting pollinators, which are essential to many ecosystems. Explore these insights further to uncover the intricate world of pollination and its impact on your beloved vegetable garden!
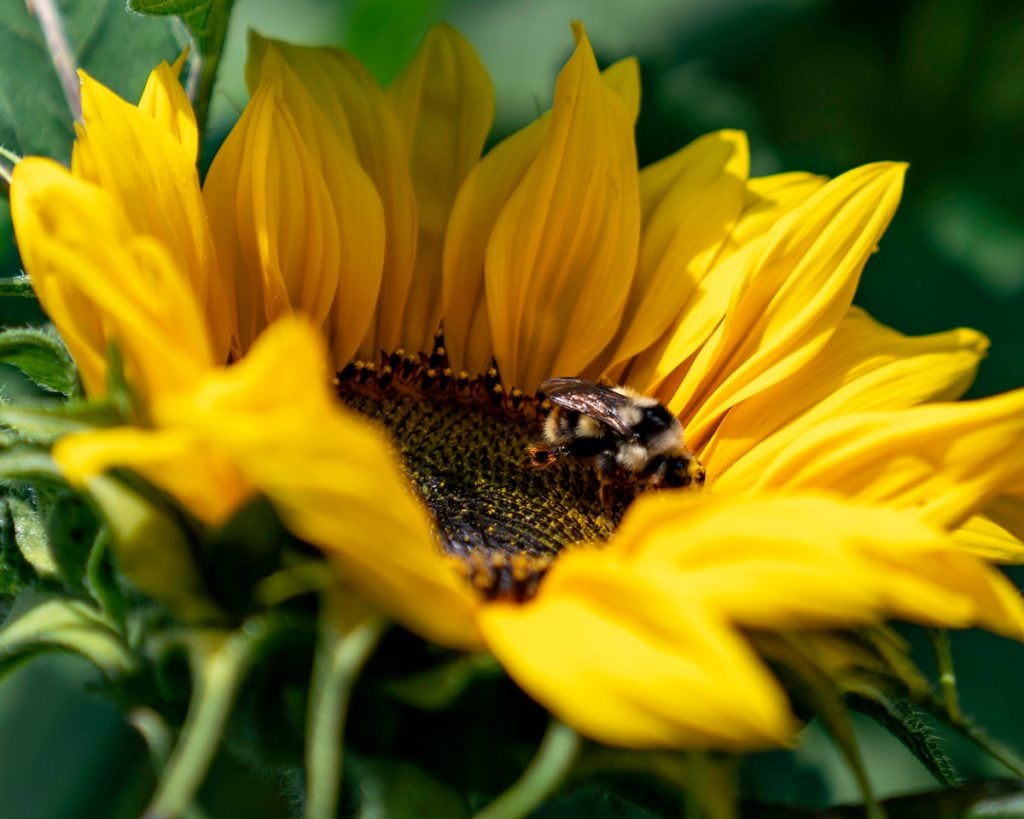

DIVE DEEPER: Click here to learn more about cultivating medicinal herbs at home
Creating a Pollinator-Friendly Environment
For those looking to enhance the productivity of their vegetable gardens, creating a pollinator-friendly environment is one of the most impactful steps you can take. By understanding the specific needs of pollinators and how they interact with various plants, beginners can easily cultivate a garden that not only thrives but also supports vital ecosystems. Among the myriad of pollinators, bees remain the most significant, being responsible for one-third of the food we consume in the United States. Thus, attracting these essential creatures is paramount.
Choosing the Right Plants:
One of the simplest yet most effective strategies for attracting pollinators is selecting the right plants. By incorporating plants that naturally appeal to bees and other beneficial insects, gardeners increase the likelihood of these pollinators visiting their gardens. Here’s a list of essential plants to consider:
- Lavender: Known for its calming fragrance, lavender is also a favorite among honeybees and bumblebees.
- Wildflowers: Diverse wildflower mixes provide a feast for pollinators, offering a variety of colors and scents.
- Herbs: Plants like rosemary, thyme, and basil not only enhance your kitchen but also attract bees when allowed to flower.
- Fruit Trees: Apple and cherry trees are excellent choices, as their blossoms provide ample nectar during spring.
Moreover, native plants are often well-adapted to local conditions and require less maintenance, making them a wise choice for beginner gardeners. Not only do they provide a reliable source of food for pollinators, but they also bolster local biodiversity, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem.
Creating Shelter and Nesting Sites:
It’s essential to recognize that attracting pollinators goes beyond just providing food; these creatures need places to rest and reproduce. Here are some practical ideas for creating suitable habitats:
- Leave Bare Ground: Some pollinators, like ground-nesting bees, require bare soil for nesting. Leaving patches of bare ground undisturbed is beneficial.
- Add Mulch and Debris: Piling up leaves, logs, or plant debris can encourage beneficial insects to blossom and offer shelter during unfavorable weather conditions.
- Install Bee Hotels: These structures can harbor solitary bees, which are excellent pollinators, by providing them with small tubes to lay their eggs.
Incorporating these elements into your garden will not only make it welcoming for pollinators but will also foster a more vibrant and productive vegetable garden. By understanding the needs of these essential creatures, gardeners can take active steps to promote their health and presence, ultimately enjoying the bountiful benefits they bring to our vegetable plots.
The Importance of Pollination in Your Vegetable Garden
Pollination is a vital process that significantly impacts the yield and quality of vegetables in your garden. Understanding how to attract pollinators is essential for beginners seeking to maximize their harvests. Notably, various species play pivotal roles in this process, including bees, butterflies, and even hummingbirds. By creating an inviting environment, you not only support these creatures but also enhance your garden’s productivity.
Understanding Pollinators
Pollinators are responsible for transferring pollen from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, thereby facilitating fertilization. This process leads to the production of fruits and seeds. In a vegetable garden, effective pollination ensures that crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash yield abundant fruits. As a beginner, knowing the type of pollinators that frequent your area can help you plan better to attract them.
Creating a Pollinator-Friendly Environment
To attract pollinators, it’s essential to cultivate a diverse garden filled with a variety of flowers. Selecting native plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season ensures a steady food source for pollinators. Additionally, incorporating plants with a variety of shapes and sizes can cater to different species. For instance, flat flowers like daisies attract hoverflies, while tubular flowers are appealing to hummingbirds.Moreover, maintaining a chemical-free garden is crucial. Pesticides can harm beneficial insects, deterring them from your garden. Instead, opt for organic gardening practices that promote a balanced ecosystem. By implementing these practices, you’ll create a thriving habitat that fosters pollination and boosts your vegetable garden’s productivity.
| Category | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Crop Yields | Increased fruit and vegetable production through effective fertilization. |
| Biodiversity Support | Encourages a healthy ecosystem by supporting diverse plant species and wildlife. |
Enhancing your knowledge about pollination can lead to more flourishing vegetable gardens. This understanding ignites curiosity and encourages sustainable gardening practices that can have lasting benefits for both your health and the environment.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn how to select the perfect herbs for your garden</
Enhancing Pollinator Activity through Best Practices
In addition to planting the right species and providing habitats, gardeners can employ best practices that enhance pollinator activity and ensure a thriving vegetable garden. Pollinators are sensitive to their environment, and small changes can lead to significant improvements in their presence. Here are some essential techniques to keep in mind:
Avoiding Pesticides:
One of the most critical steps in fostering a welcoming environment for pollinators is to minimize or completely eliminate the use of chemical pesticides. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, pesticides can have detrimental effects on bees and other beneficial insects, leading to decreased pollination rates. Instead, consider organic alternatives such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, which are less harmful to pollinators. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can also help keep pests in check without risking harm to these vital creatures.
Practicing Crop Diversity:
Diversity is key when it comes to attracting different species of pollinators. By growing a range of vegetables, fruits, and companion plants, gardeners create a rich tapestry that appeals to various pollinators. For instance, planting a combination of flowering crops like zucchini, cucumbers, and melons, alongside vibrant sunflowers or marigolds, not only attracts more bees but also improves pollination efficiency. A study conducted by the University of California found that crop diversity significantly increases pollinator visitation rates, ultimately resulting in enhanced harvest yields.
Providing Water Sources:
Like all living creatures, pollinators need water to survive. A simple birdbath, filled with fresh water and replenished regularly, can become an oasis in your garden, attracting thirsty bees and butterflies. Add stones or pebbles to the water source, ensuring the insects have safe perches to drink from without the risk of drowning. This small effort can go a long way in building a pollinator-friendly sanctuary.
Timing Your Floral Displays:
Consideration of bloom times can also maximize your garden’s appeal to pollinators throughout the growing season. By planting a succession of blooming plants that flower at different times, you ensure a continuous food supply for pollinators. Early spring flowers like crocuses and bluebells can provide vital resources after a long winter, while late-blooming plants such as asters and goldenrod sustain pollinators as they prepare for winter. A well-planned seasonal succession ensures sustenance for pollinators at critical times, reinforcing their presence in your garden.
Creating a Pollinator Pathway:
Linking your vegetable garden with other nearby green spaces can create a pollinator pathway, serving as a corridor for bees and other pollinators to travel between food sources. This can include planting a series of pollinator-friendly plants in adjacent areas or coordinating with neighbors to establish a network of gardens that support one another. The Pollinator Partnership suggests that even small efforts in urban settings can result in significant impacts, promoting essential habitats amid concrete landscapes.
By embracing these practices, beginner gardeners not only enhance their vegetable garden’s productivity but also join a broader initiative to support biodiversity. As more gardeners recognize the importance of cultivating relationships with pollinators, the cumulative effect leads to healthier ecosystems and a more robust food supply for communities.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn about vertical gardening techniques
Conclusion
Pollination is a pivotal process in maintaining the health and productivity of your vegetable garden. By understanding the importance of pollination and implementing effective strategies to attract pollinators, even beginner gardeners can cultivate vibrant and bountiful gardens. Our five techniques—from minimizing pesticide use to creating a pollinator pathway—provide actionable steps to enhance your garden’s biodiversity and ecological balance.
Furthermore, as we witness alarming declines in pollinator populations, your garden can serve as a sanctuary that contributes to the larger environment. The ripple effect of your actions can lead to improved harvest yields while supporting the vital roles played by bees, butterflies, and other insects in our ecosystems. Emphasizing crop diversity not only attracts a variety of pollinators but also enriches your gardening experience with colorful displays and enhanced flavors in your produce.
As you embark on this gardening adventure, consider the profound connection between plants and pollinators, propelling both your personal garden and local ecosystems towards sustainability. For those eager to learn more, numerous resources and communities are available, fostering knowledge-sharing and support in this essential endeavor. By becoming an advocate for pollinators, you are not only nurturing your vegetable garden but also contributing to a healthier planet for generations to come.